Describe the Histology of Compact and Spongy Bone
The compact bone is the main structure in the body for support protection and movement. Spongy bone contains large marrow spaces defined by shelves and spicules of bone.
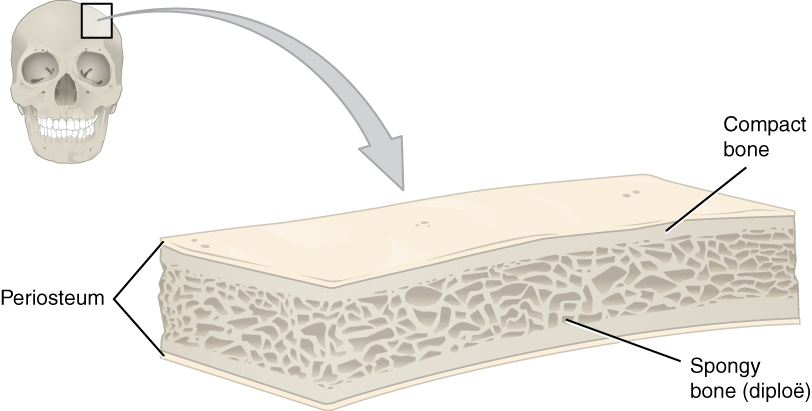
Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology
There are open spaces that weave in and out of the bone creating a spongy resemblance.

. Forms the diaphysis shaft of long bones. -All osteocytes close to bone marrow. They become osteocytes the cells of mature bone when they get trapped in the matrix.
The term spongy comes from the fact that it is a highly vascularized and porous tissue. There are three types of cells that contribute to bone homeostasis. FRD1021 Radiologic Biology 1 Lecture 12.
Compact bone or cortical bone mainly serves a mechanical function. The structural layout of bone can be classified in one of the following groups. Trabeculae are spaces created in the tissue by thin areas of osteoblast cells.
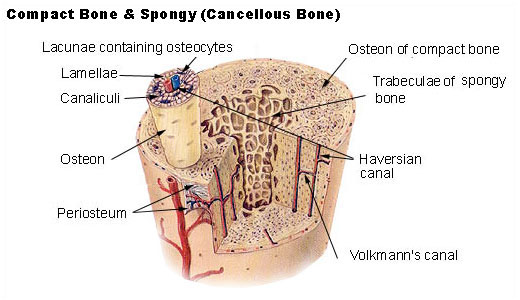
1 The structural unit of compact bone is the osteon or Haversian system which consists of concentric tubes of bone matrix the lamellae surrounding a central Haversian canal that serves as a passageway for blood vessels and nerves. List the cell types present in bone tissue and describe their functions Describe and compare the structural features of compact and spongy bone Outline the process of bone formation Describe remodelling and repair of bone Slide 4 Course. The spongy bone and medullary cavity receive nourishment from arteries that pass through the compact bone.
Are osseous tissue bone. It is thick and dense. Made up of trabeculae.
-Few osteons and no central canals. Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of osseous tissue Figure 636. Very small amount of calcium is present in them.
The osteocytes in spongy bone are nourished by blood vessels of the periosteum that penetrate spongy bone and blood that circulates in the marrow cavities. These bones are cylindrical in shape. Due to the strong nature of compact bone compared to spongy bone it is the preferred tissue for strength.
The arteries enter through the nutrient foramen plural foramina small openings in the diaphysis Figure 615. Osteocytes can be seen in layers in adult spongy bone. Compact bone histology.
This shows the architecture of compact bone which is designed to nourish and regulate osteocytes and bone matrix. Osteogenic cells develop into osteoblasts. Either trabecular cancellous or spongy or compact.
Internal circumferential lamellae of compact bone. Compact Bone IMAGE 1. There are two types of bone tissue.
This is the area of bone to which ligaments and tendons attach. The dense material is of uniform smooth texture without any cavity within is known as the compact bone. However compact bones also serve a.
Osseous tissue is maintained by bone-forming cells called osteoblasts and cells that break down bone called osteoclasts. Compact and spongy bone are both mineralized collagen. Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces while spongy bone also called cancellous bone has open spaces and is supportive but also lightweight and can be readily remodeled to accommodate changing body needs.
Ans1Compact and spongy bones are the two main types of osseous tissues. Osteoblasts are bone-forming cell osteoclasts resorb or break down bone and osteocytes are mature bone cells. Compact bone slowly changes according to the stress tension and other mechanical forces.
2Compact View the full answer. Also called as cancellous bones. A Perforating or Volkmanns canals lie at right angles to.
Almost 80 or above weight of human skeleton is contributed by compact bones. YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE. Concentric lamellae of osteon or haversian system.
Spongy bone is also called cancellous or trabecular bone. Calcium is present in high quantity in them. It can be remodeled all throughout life to withstand stress.
COMPACT BONE HISTOLOGY. Thin plates of bone called trabeculae and spaces filled with red bone marrow. The inner space is lined by osteoblasts and osteoclasts called the endosteum.
SPONGY BONE HISTOLOGY. Describe the histology of compact and spongy bone. Tissue that gives strength and structure to bones.
-Provides strength with minimal weight. The rest 20 weight of the skeleton is contributed by spongy bones. Also called as cortical bones.
-Trabeculae develop along bones lines of stress. Osteoclasts engage in bone resorption. Histologically spongy bone is comprised of anastomosing strips of slender bone known as trabeculae that enclose marrow and blood vessels.
Made up of osteons. Center canal or Haversian canal of an osteon. Compact Cortical Bone Spongy Cancellous Bone.
Spongy bone is used for more active functions of the bones including blood cell production and ion exchange. They are compact heavy and tough in nature. Osteoblasts are cells that make new bone.
It is found in the long bones and it is surrounded by compact bone. Compact bones fills the outer layers of most of the bones. Bone is made up of compact tissue the hard outer layer and cancellous tissue the spongy inner layer that contains red marrow.
Fchsacae Learning Outcomes At the completion of this lecture you will be able to. Forms the epiphyses ends of long bones. The shaft of the long bone like femur has a cavity known as a bone marrow cavity.
Compact bone is described as what is seen and is the outer type of the bone. The names imply that the two types differ in density or how tightly the tissue is packed together. Compact bone is dense and composed of osteons while spongy bone is less dense and made up of trabeculae.
An equilibrium between osteoblasts and. It makes up the outer cortex. The compact bone is opaque there is no way to see inside the bone without cutting it open.
This type of bone is located between layers of compact bone and is thin and porous. External circumferential lamellae of compact bone. Trabecular bone also known as cancellous bone or spongy bone mainly serves a metabolic function.
They are spongy light and soft in nature. The cavity is walled by dense material. It forms the relatively softer core of the bones that is filled with marrow.
Overall osteon or Haversian system of bone.
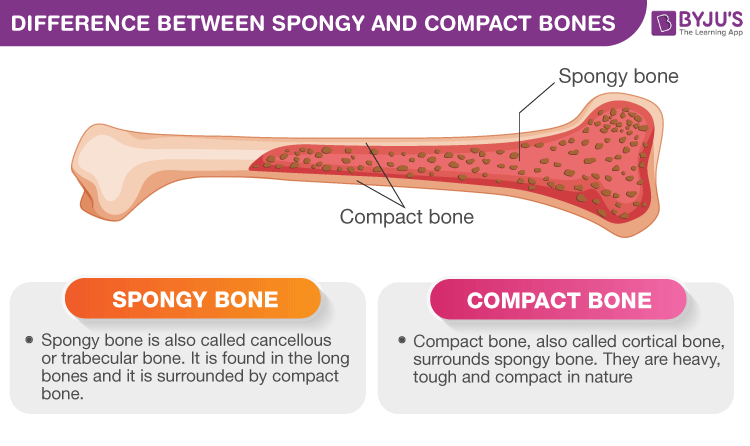
Difference Between Spongy And Compact Bones Spongy Vs Compact

Difference Between Compact Bone And Spongy Bone Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
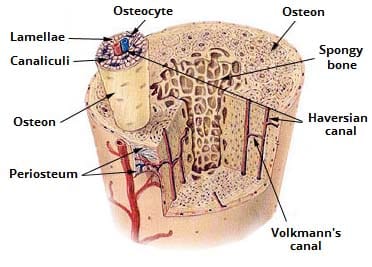
Ultrastructure Of Bone Components Structure Teachmeanatomy
Difference Between Compact And Spongy Bone Definition Features Function

Spongy Bone Containg Red Bone Marrow Anatomy Bones Basic Anatomy And Physiology Human Bones Anatomy

6 3 Bone Structure Anatomy Physiology

Lab 5 Bone Histology Compact Spongy Bone Flashcards Quizlet

6 3 Bone Structure Anatomy Physiology

Bones Structure And Types Youtube

Cancellous Bone Anatomy Britannica

Structure Of Bones Biology For Majors Ii
Difference Between Compact And Spongy Bone Definition Features Function

Bone Spongy And Compact Structure Of Spongy Bone Bones Anatomy Bones Human Skeleton Anatomy

Spongy Bone Cancellous Bone Definition Function Biology
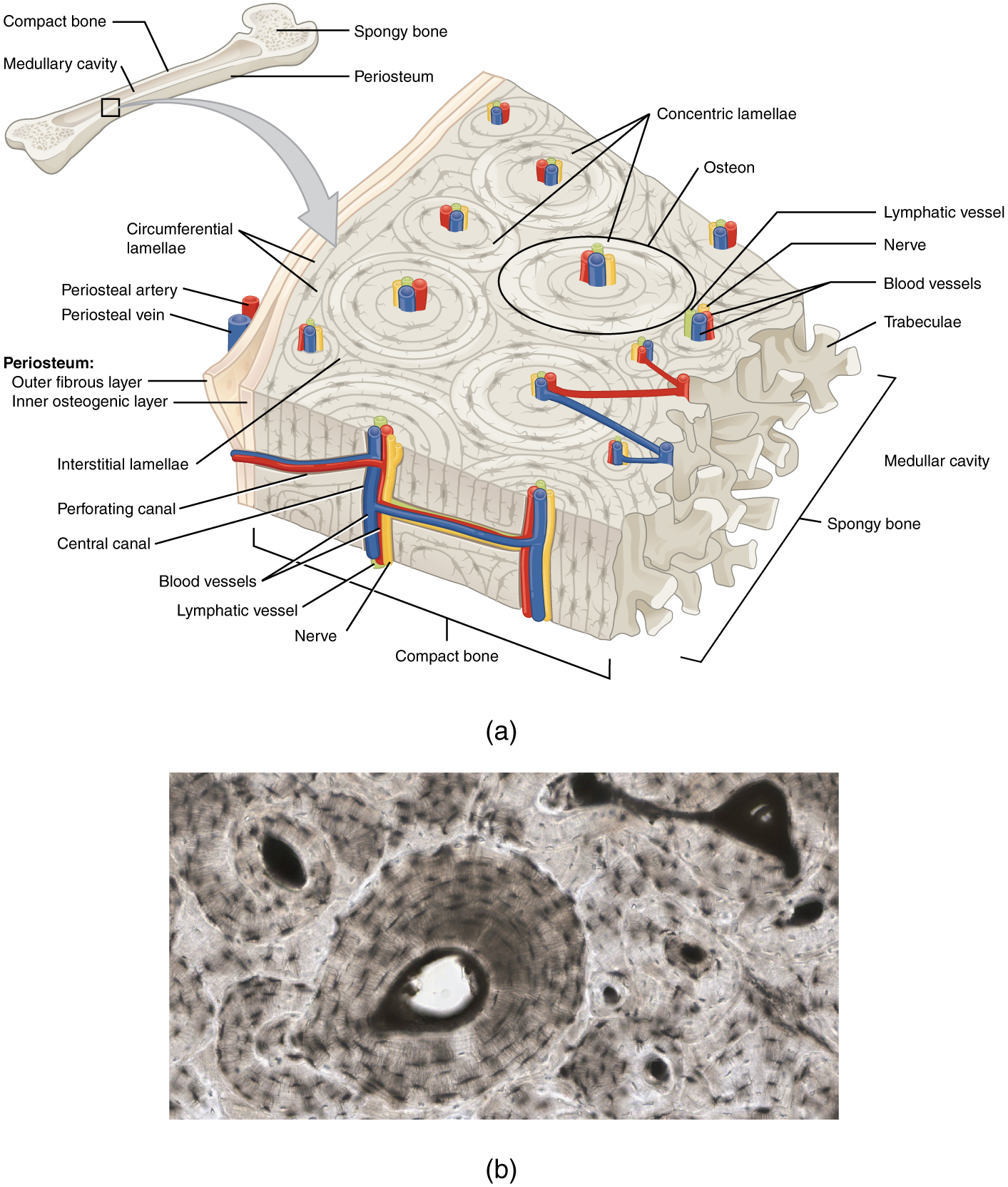
Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology

Compact Bone Definition Structure Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Comments
Post a Comment